Alba Marquez: “Data-driven approach holds significant promise for managing landscapes and preventing wildfires”

Wildfires, while being a crucial factor in landscape transformation and vegetation succession, also pose significant threats to socio-ecological values. Sicily, Italy, has been a witness to the impact of wildfires on its delicate ecosystems.
In response to these challenges, a new article led by BC3 researcher Alba Marquez develops a fire risk model for Sicily to assist in managing the ecosystems most susceptible to wildfires. By creating a comprehensive fire risk mapping model, the team aims to effectively equip stakeholders with valuable insights and tools to mitigate fire hazards.
This study integrates various data-driven models and analyzes how to manage better vulnerable ecosystems affected by wildfires using k.LAB, which enables seamless integration of input data. Other advanced methods, such as GIS, Remote Sensing, and Bayesian Network algorithms, were harnessed to gain deeper insights into fire risk probability.
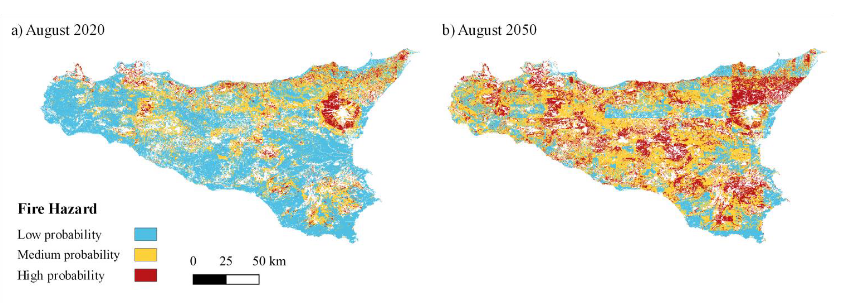
The research revealed that the wildland area with high fire probability occurrence will change from 8% to 27%, between 2020 to 2050 and a staggering 45% of vulnerable areas in the region are projected to be at high risk of fire danger by 2050. These findings underscore the urgent need for proactive wildfire management strategies.
“We have studied the historical fires from the years 2000 to 2020, encompassing a dataset of 14,491 instances. Through our research, we have identified key factors significantly shaping fire occurrences in Sicily. These factors include atmospheric temperature, duration of rainless days, and the specific fuel types present, all playing pivotal roles in influencing fire dynamics.” (Alba Márquez Torres, BC3 researcher)
Recognising the importance of making research results understandable to all stakeholders, the research team incorporated qualitative risk indexes into their model outputs. This approach ensures that even non-technical individuals can grasp the implications of the study and actively participate in decision-making processes.
- “Data-driven approach holds significant promise for managing landscapes and preventing wildfires, especially in the context of climate change. By providing daily, spatially explicit results, fire risk models empower decision-makers to adopt proactive prevention measures.” (Alba Márquez Torres, BC3 researcher)
